MRI Vascular Test
Vascular magnetic resonance imaging The natural contrast of flow void can be used to diagnose the intimal flap and dilated contours of an aortic dissection and protruding plaques of atherosclerotic diseases. It also allows for the detection of congenital and acquired vascular abnormalities. Although MRI can be expensive, vascular MRI has many advantages. It is noninvasive, multiplanar, does not require contrast materials, and it may even replace technically limited ultrasonography. MRI is able to define anatomy and measure blood flow. It can also be used in serial examinations for following diseases and their response to treatment. The future research on tissue characterization of atherosclerotic plaque may help to diagnose and treat this common disease. It would prove to be beneficial not only for chemical, but also for metabolic, such as tissue perfusion of the heart or other viscera. MRI is certain to play a significant role in the diagnosis of cardiovascular disease.
These so-called vascular malformations can be diagnosed with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasonography, and/or computerizedtomography (CT scanning). This allows doctors to see more clearly the structures of nearby and affected blood vessels.
According to interventional radioologist and director of Yale Medicine’s HHT Program, vascular malformations can cause a variety of symptoms.
If someone has suggestive symptoms or if other relatives have a history of vascular malformation, they will be referred to the specialist.
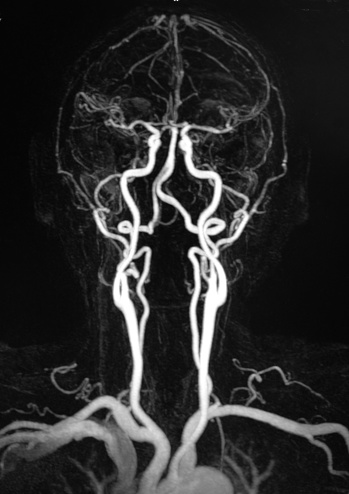
People are referred for diagnosis of vascular malformation when they display suggestive symptoms, when other family members have a known inheritable vascular malformation and/or when earlier CT or MRI imaging indicates a possible problem.